DIABETES
ENDODONTICS
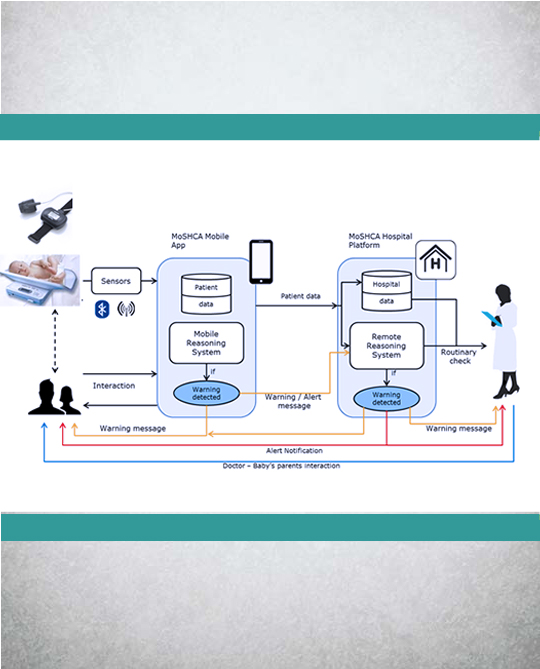
PREMATURE BABIES
REHABILITATION
MEDICAL EQUIPAMENT MAINTENANCE
| Goal: Complex equipment failure prediction (e.g. Magnetic Resonance Imaging devices, Computer Tomography scans). |
|---|
The use of complex medical equipment (Magnetic Resonance Imaging – MRI, Computer Tomography – CT, Positron Emission Tomography – PET-CT ) has been crucial for patient diagnosis. Such equipment is known to be complex, composed of several pieces and subsystems, all of them subjected to high safety constraints, since they are using sensible technology regarding human health. Thus, if there is a minimal deviation of a given configuration parameter of the equipment component, the equipment sets up an alarm and stops. Nevertheless, when a machine fails, it causes many problems in the clinical service. Thus, a desired situation is to monitor the medical equipment so that failures can be predicted. We use sequence learning to learn failure patterns from even logs produced by the components of the machines. Patterns are used in a case-based reasoning system to predict failures. On the other hand, we explore a probabilistic approach to create predictive models based on the exploitation of existing maintenance registers for the estimation of failure rates and internal cause-effect relationships to build those models. |
| Goal: Workflow monitoring for equipment repair. |
|---|
|
AMBULANCE COORDINATION
| Urgent patient transport. |
|---|
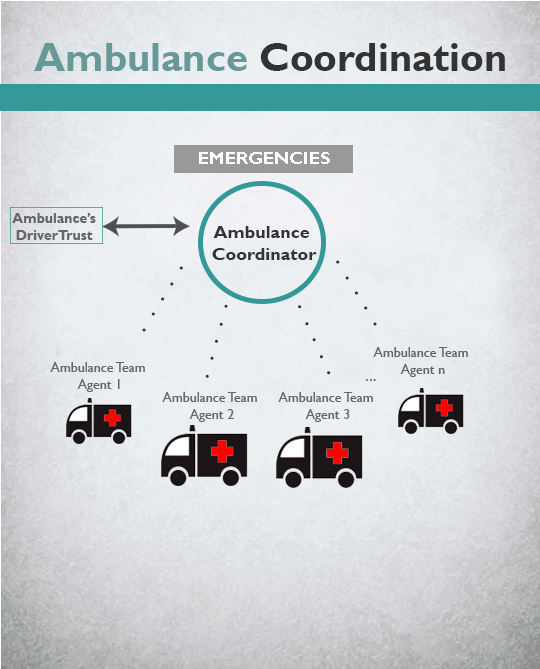
Emergency transportation on specialized vehicles is needed when a person’s health is in risk of irreparable damage. In rural regions, studies have shown that ambulance teams have different response times, mainly because of the drivers’ expertise. The challenge for the regional authorities is to appropriately coordinate their resources to continuously improve response time, taking into account the resources needed and driver expertise. In response, we developed a multi-agent system that maintain the real distributed organization of resources. To solve the assignment problem (which ambulance agent attends a patient request), we use an auction mechanism and a region coverage algorithm. Driver skills are represented by trust, and ambulance response times are modulated by them. |
| Programmed patient transport. |
|---|
|